We currently are using two molecular testing technologies to examine and troubleshoot wastewater biomass. Both tests use the 16s region found in all bacterial cells and the best way to identify bacteria down to the species level. Each is detailed below:
Microbial Community Analysis
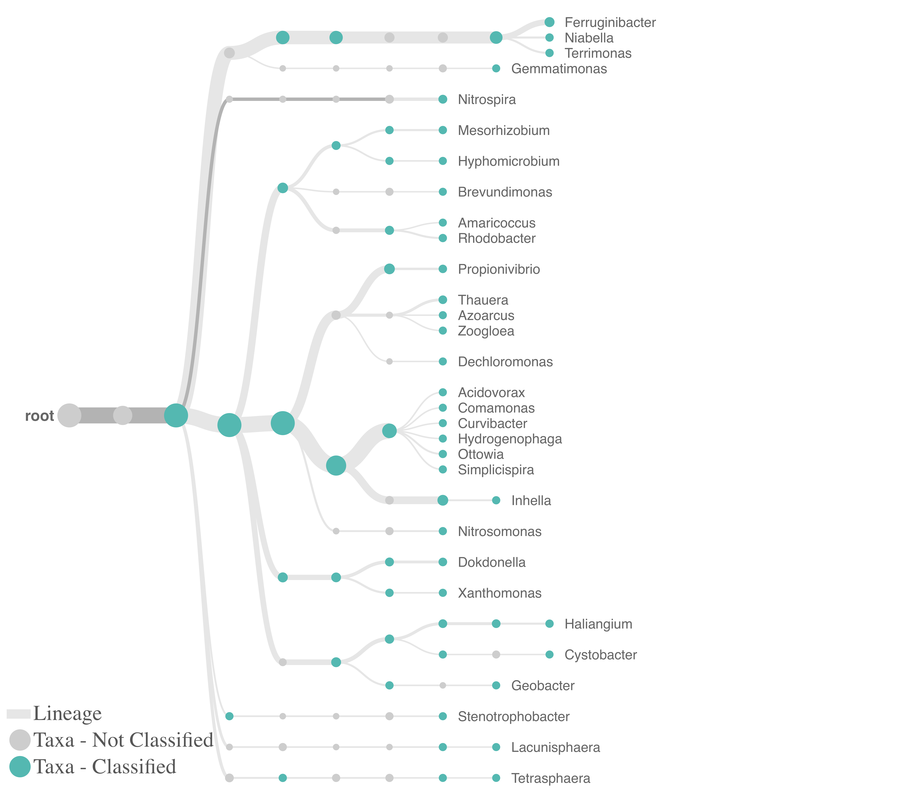
Using high throughput sequencing, Aster Bio can take an MLSS sample and conduct a microbial census. This test gives the relative frequency of each organism with accuracy down to the genus level. Microbial community analysis picks up all genetic material present, even organisms that do not grow on traditional microbiological media plates. The results are often presented as a Sankey Chart with relative frequency and Observed Taxonomic Units (OTU) ~ which are akin to older plate count CFU numbers. The Microbial Community Analysis is a more complex test, but gives deep information never before available on what is in the system and doing the work. The test shows how changes in operations impact the total microbial populations and is also used to develop customized qPCR tests which are specific for "keystone" organisms.
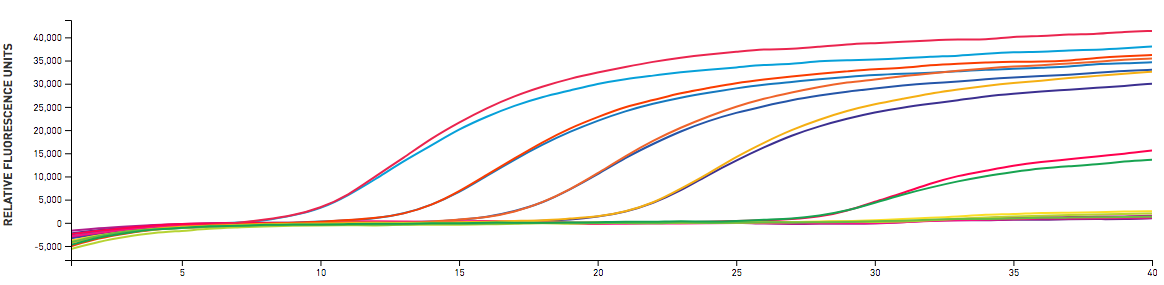
After running Microbial Community Analysis tests, we can pick out key organisms related to good and bad operational efficiency. qPCR can test for AOB/NOB (nitrifiers), specific filamentous bulking organisms, SRB, and even non-filamentous bulking organisms. Once we select target organisms, Aster Bio's lab develops custom qPCR tests that can detect and quantify only matching 16s sequences in MLSS samples. qPCR testing can screen for multiple taxonomic units in each run. With its combination of speed, accuracy and lower cost, qPCR is designed for routine monitoring - where the Microbial Community Analysis is more of a high detail periodic monitoring test. Key to successful use of qPCR technology is having the right tests for your system's MLSS and the ability to adapt the output information into daily operations. As you can see from the output below, qPCR amplification real-time data requires some processing to make actionable reports.


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed