- Understanding Non-Filamentous Bulking:
- Filamentous bulking occurs due to excessive growth of filamentous bacteria in WWTPs.
- Ideally, there should be a balance between filamentous bacteria and floc-forming bacteria.
- In moderate amounts, filamentous bacteria contribute to AS settle-ability by providing a structural base for robust floc formation.
- The Role of EPS (Extracellular Polymeric Substances):
- EPS is crucial for floc formation in suspended growth and biofilms.
- It consists of polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids, and metabolic byproducts.
- EPS protects cells and accumulates nutrients (N, P, metals).
- Proper EPS levels are essential for solids removal and phosphate removal.
- The Transition to Excess EPS:
- Excess EPS leads to problems:
- Waste solids retain more bound water.
- Dewatering becomes difficult.
- Secondary clarifiers may have floating scum and poor compaction.
- Major contributors to non-filamentous bulking:
- Thauera: Common in industrial activated sludge.
- Zooglea: More common in domestic wastewater.
- Azoarcus: Less common but efficient denitrifiers.
- Excess EPS leads to problems:
- Control Strategies:
- Nutrient Adjustment:
- Turn up nutrients (N or P) if not already optimal. If C:N:P ratio is in the target zone, adding additional nutrients will not help with bulking.
- Waste Solids Management:
- Remove excess EPS through waste activated sludge (WAS).
- Be cautious as it increases the F/M ratio.
- Bioaugmentation:
- Increases viable microorganisms in the mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) breaking bottlenecks created by overgrowth of high EPS producing organisms.
- Aster Bio has identified and produced cultures having the ability to degrade EPS via extra-cellular enzymes and form beneficial capsular polymers that function much like chemical cationic coagulants.
- Nutrient Adjustment:
- Monitoring and Early Detection:
- Use molecular tests including qPCR to detect changes in Zooglea populations.
- Look for signs of increased soluble BOD loadings at the influent.
|
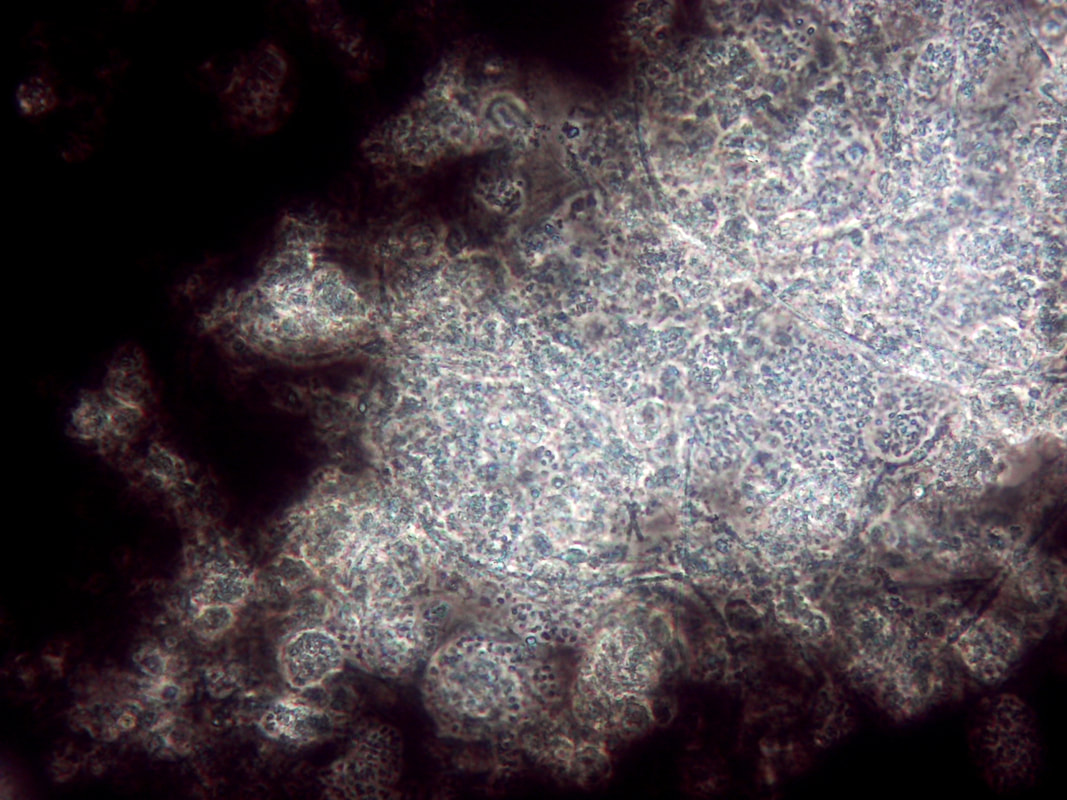
Non-filamentous bulking in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) can be a challenging issue, affecting the quality of the final effluent. In the photo above, note the rounded colonies that appear to have more "gel" between the cells - these are high EPS zones. Also, the above photo is using India Ink. The carbon particles in the ink do no penetrate high EPS floc which proves that you have excess EPS and non-filamentous bulking. Let’s explore strategies for controlling this phenomenon:
Are predatory protozoa harmful to bacteria populations in your wastewater treatment plant?3/26/2024
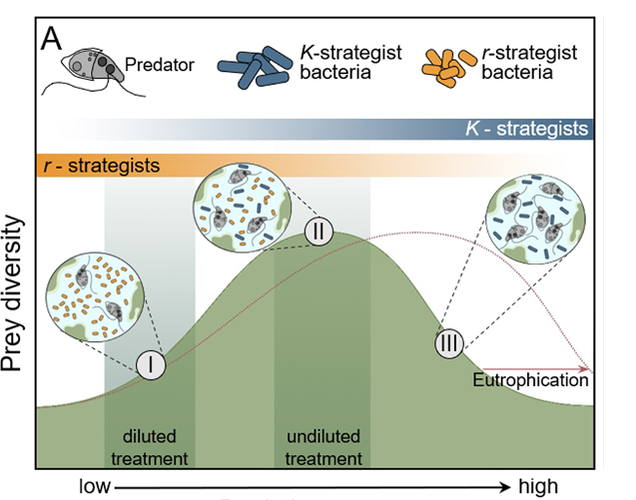
Protozoa are eukaryotic residents of wastewater treatment plants that serve as primary predators of bacteria. (Some protozoa are free-living and not predatory). Since protozoa are much larger than bacteria and easily recognized by shape and motility, we use their diversity and populations as indicators of system health.
Since the protozoa “eat” bacteria and bacteria are the organisms that remove pollutants, are the protozoa detrimental to treatment efficiency? Protozoa populations and diversity increase as you move along the growth curve where bacterial populations are higher and water quality improves. The protozoa feed on both free bacteria in solution and by grazing on the biofilm/floc. We know that by removing free bacteria in solution, the protozoa decrease turbidity and TSS. When grazing on floc, the protozoa contribute to biofilm turnover. We are concerned that protozoa predation will damage slower growing microbial populations such as Ammonia Oxidizing Bacteria (AOB) and Nitrite Oxidizing Bacteria (NOB) – Nitrifiers. Looking at research, we find the following:
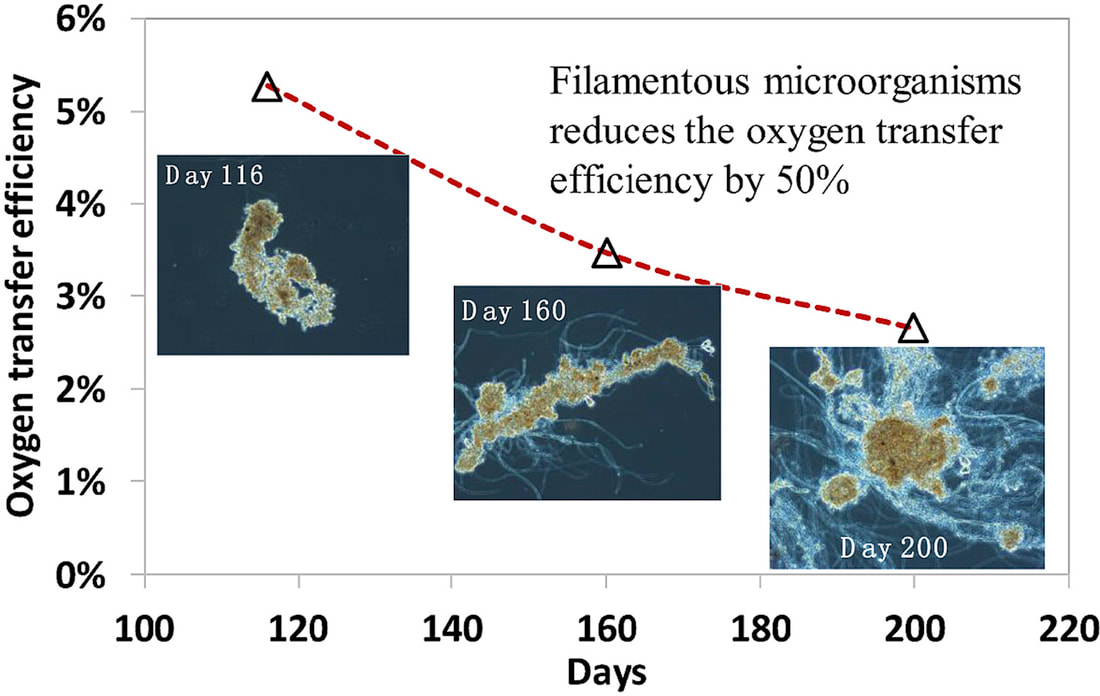
Good articles on protozoa impact on wastewater microbial populations: Burian, A., Pinn, D., Peralta-Maraver, I. et al. Predation increases multiple components of microbial diversity in activated sludge communities. ISME J 16, 1086–1094 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-021-01145-z Wu L, et al. Global diversity and biogeography of bacterial communities in wastewater treatment plants. Nat Microbiol. 2019 Jul;4(7):1183-1195. doi: 10.1038/s41564-019-0426-5. Epub 2019 May 13. Erratum in: Nat Microbiol. 2019 Dec;4(12):2579. PMID: 31086312. Pogue AJ, Gilbride KA. Impact of protozoan grazing on nitrification and the ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizing bacterial communities in activated sludge. Can J Microbiol. 2007 May;53(5):559-71. doi: 10.1139/W07-027. PMID: 17668014. This topic was brought to my attention last week when a facility that I am working with noticed that Thiothrix filaments appeared to be reducing oxygen transfer efficiency in the aeration basin. While low D.O. promoting filamentous growth is well known, I was not familiar with how much filamentous bulking can reduce OTE.
Oxygen Transfer Efficiency (OTE) refers to how effectively oxygen is delivered and dissolved in water under specific conditions. Systems are designed based on predicted OTE as conditions vary in working wastewater treatment systems. When you compare floc forming sludge (FFS) versus filamentous bulking sludge (FBS), OTE decreases by up to 50%. Filament length also impacts the results with longer filaments, such as Thiothrix, having more impact on OTE than short filament that do not extend from the floc. The studies proposed that the loss in transfer efficiency related to:
Good reference articles on the topic: Ken Campbell et al. Filamentous organisms degrade oxygen transfer efficiency by increasing mixed liquor apparent viscosity: Mechanistic understanding and experimental verification https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0043135420301068 Guoqiang Liu et al. Formation of filamentous microorganisms impedes oxygen transfer and decreases aeration efficiency for wastewater treatment https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0959652618311521 Xianwei Wu et al. Thiothrix eikelboomii interferes oxygen transfer in activated sludge https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0043135418310364 Archaea are not bacteria! While still unicellular, they are as different from bacteria as a they are from you (a Eukaryote). Some cool facts about Archaea:
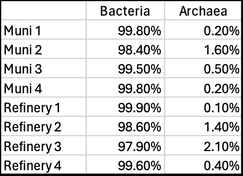
Last week, Paul Campbell used qPCR to test a random sample of four municipal treatment systems (some with upstream anaerobic digesters) and four industrial aerobic treatment systems. Here are the results (% of total biomass) Note the relatively low levels of archaea in these wastewater treatment systems. Those with higher levels of archaea tended to be those with upstream anaerobic digesters where methanogens are very important. Or systems with longer sludge ages where we also find more niche bacteria in the MLSS. While low in frequency, these archaea may perform some vital functions, but this is not known. We are continuing to use molecular tools to learn more about the wastewater microbial community and will report more of our results as we discover new pathways and interesting organisms.
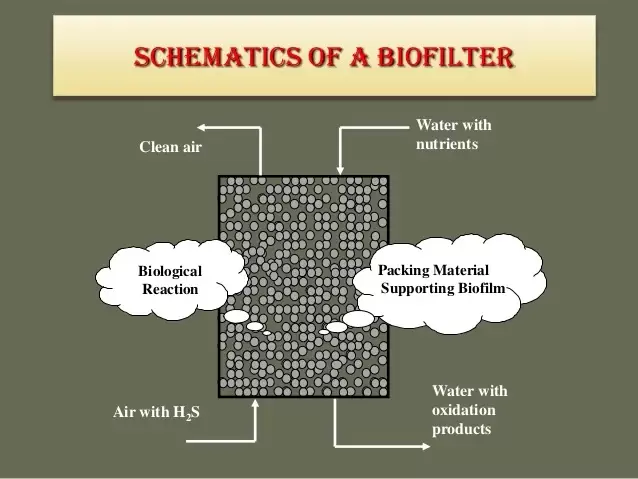
Biofilters consist of a bed of organic material, such as compost, wood chips, or synthetic materials, that provides a substrate for the growth of microorganisms. The media's surface area is crucial for microbial colonization and the adsorption/removal of odorous compounds.
Microbial Colonization:
Biofilter systems are often chosen for their sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and ability to handle a wide range of odorous compounds. However, the efficiency of biofilter treatment can be influenced by factors such as temperature, pH, nutrient availability, and the specific characteristics of the odorous compounds being treated. Regular monitoring and proper maintenance are essential for optimal performance. Organic acids are formed under anerobic conditions where bacteria grow under what we call fermentative conditions (bacteria using organic compounds as a terminal electron acceptor to get energy). Common sources of organic acids include – collection systems, equalization tanks, sludge layers in lagoons, and even anaerobic digesters. If there are sulfides present, organic acids are a key part of what we call “septic” water. Biological nutrient removal systems require organic acids to function properly – especially in the case of phosphorus removal. At the same time, organic acids can also be a problem component in wastewater operations. Here's how organic acids contribute to these processes:
Source of Carbon and Energy for Microorganisms: Organic acids serve as a crucial carbon source for microorganisms in biological treatment systems. Microorganisms use organic acids as a substrate for their growth and metabolism. This is particularly important in aerobic treatment processes like activated sludge, where microorganisms need organic carbon to thrive. Microbial Metabolism and Nutrient Removal: Microorganisms metabolize organic acids through various biochemical pathways, contributing to the breakdown of complex organic compounds. This metabolism results in the production of microbial biomass and energy for microbial activities. As microorganisms grow and reproduce, they assimilate nutrients, aiding in the removal of nitrogen and phosphorus compounds from the wastewater. In the case of Bio-P organisms, the microbes uptake organic acids under anaerobic conditions which are utilized later under aerobic conditions. Energy is then stored as intracellular phosphate which also powers the uptake of organic acids under anaerobic conditions. Organic acids also are often the soluble carbon source for denitrification. Encourage Filamentous Growth: High organic acids can depress D.O. levels in the influent zone of activated sludge systems. The low D.O. coupled with soluble substrate creates conditions favoring several types of common filamentous bulking organisms. Preventing the low D.O. zone with high organic acids, is why step feed systems are often effective in controlling bulking in plug flow systems. pH Buffering: Organic acids can act as natural pH buffers in wastewater systems. In biological treatment processes, the production of organic acids by microbial activity can help maintain a suitable pH environment for the microorganisms. This is crucial because microbial activity is often sensitive to changes in pH, and maintaining an optimal pH range is necessary for efficient treatment. Enhancement of Anaerobic Digestion: In anaerobic digestion processes, organic acids are intermediates in the breakdown of complex organic matter. Later, archaea methanogens convert organic acids into methane and carbon dioxide. The production of organic acids is a key step in the hydrolysis and acidogenesis phases of anaerobic digestion. Inhibition and Toxicity: On the flip side, excessive accumulation of certain organic acids can have inhibitory effects on microbial activity. Some organic acids, especially those with low pH values, can be toxic to microorganisms and may impact the efficiency of the treatment process. Therefore, it's essential to carefully manage the concentration and types of organic acids in the wastewater. Formation of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS): Microorganisms in biological treatment systems produce extracellular polymeric substances (EPS), which play a role in the formation and stability of biofilms. These substances, which include organic acids, help in the adhesion of microbial communities to surfaces, promoting the formation of biofilms in biofilm-based treatment systems. Excessive organic acids can also trigger over-production of EPS leading to non-filamentous or Zoogleal bulking. |
AuthorErik Rumbaugh has been involved in biological waste treatment for over 20 years. He has worked with industrial and municipal wastewater facilities to ensure optimal performance of their treatment systems. He is a founder of Aster Bio (www.asterbio.com) specializing in biological waste treatment. Click to set custom HTML
Archives
April 2024
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed